AssignmentGPT Blogs
The rapid growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has revolutionized our lives, integrating everyday objects like smart refrigerators and security cameras with complex systems such as industrial machines and autonomous vehicles. Equipped with sensors, software, and other technologies, these devices communicate and communicate with each other over the Internet, creating a vast network that brings unprecedented comfort and performance but also this network significant security challenges arise· IoT security is the processes and policies used to protect these devices from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. This article examines IoT security needs and challenges, providing insights into how they can be improved to protect against emerging threats.
Quick Summary
IoT security is important because the proliferation of connected devices from smart home appliances to industrial appliances pose significant security challenges These devices are vulnerable to attacks that can lead to data breaches, service disruption, or major cyberattacks. Improving IoT security addresses key challenges such as remote exposure, resource constraints, weak passwords, and lack of encryption. Strategies include implementing robust security measures during design, regular updates, strong authentication, network segmentation, and customer education. Organizations can take a holistic approach, combining security on devices with comprehensive network security practices to mitigate risk and protect the extended IoT ecosystem.
What is IoT Security?
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are computers connected to the Internet, such as connected security cameras, smart refrigerators and WiFi-enabled cars. IoT network security is the process of protecting these devices and ensuring that they do not pose any threats to the network.
Everything on the Internet is subject to attack at some point. Attackers attempt to remotely compromise IoT devices using a variety of methods, from stealing credentials to exploiting vulnerabilities. Once an IoT device is controlled, attempts can be made to use it to steal data, launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, or compromise the rest of the network
IoT security can be particularly challenging because many IoT devices are not built with robust security features; often the manufacturer focuses on features and usability rather than security, allowing devices to reach the market faster
Why is IoT security important?
Companies are increasingly using IoT and OT devices to improve efficiency and increase visibility of their operations. As a result, a growing number of network devices used in corporate networks acquire critical data and critical systems.
These devices often have security issues that make them vulnerable to attack and put the rest of the organization at risk. For example, cyber threat agents often gain access to an organization’s network by targeting unsecured printers, smart lights, IP cameras and other connected devices and then, they can take over the network have access to critical equipment and sensitive data and ransomware and/or double boost -There can be cyber-attacks that can render a business network useless
To protect a company from cyber threats, all devices connected to the company network must be secured. IoT network security is a key component of a corporate cybersecurity strategy because it limits the risks posed by these insecure, connected devices.
IoT Security issue and challenges
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing various aspects of our lives, bringing connected devices and systems together for efficiency and convenience. However, this integration presents significant security challenges. Let’s explore each of the listed IoT security issues and challenges:
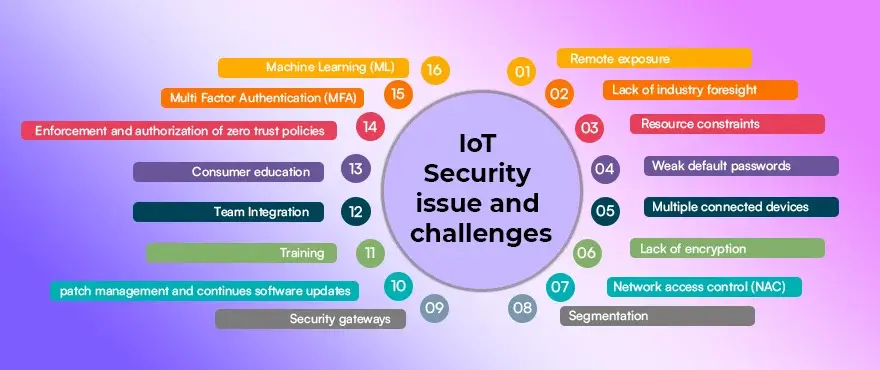
1. Remote exposure
The obvious prerequisite for remote sensing and setup is connectivity and accessibility. This leads to remote exposure and adds complexity to the IoT security landscape by requiring strong encryption, authentication mechanisms and regular security updates to ensure that IoT devices remain secure from remote threats. Internet-based and remotely accessible IoT devices can control devices remotely, as well as unauthorized, data breaches etc. Devices are vulnerable to hackers With the growing use of remote work and IoT , there are additional challenges to ensuring the security and privacy of data transmitted between remote devices and networks.
2. Lack of industry foresight
As more IoT devices are connected, and new devices are developed and released, companies take proactive steps to anticipate and address security challenges to create connected assets and intellectual property or consumers securing operational data With the right industry insights and proactive measures that can increase productivity that pays off, the industry is likely to face increased IoT security challenges and potential violations. The rapidly evolving and interconnected IoT devices pose major problems for data and privacy protection. Businesses should make it a priority to invest in robust security measures to stay ahead of potential threats and ensure the security and reliability of their IoT-connected devices.
3. Resource constraints
Many IoT devices have low power consumption, memory, and battery life, making it difficult to implement complex security measures such as complex encryption algorithms, regular software updates, etc. Resource restrictions Prevent IoT devices from performing security scans or monitoring and properly addressing potential security breaches . These limitations can make IoT devices vulnerable to cyberattacks, making them attractive to hackers looking to exploit weaknesses in their security. Developers and manufacturers should find a new solution to balance security needs with the resource constraints of IoT devices.
4. Weak default passwords
Weak passwords can easily be guessed or cracked, making IoT devices easy to access or control without authorization. This can lead to security risks such as data breaches and privacy violations. A strong and unique password ensures that IoT devices are secure and protects against potential threats. Weak passwords can make it easier for hackers to gain access to other connected devices and networks, potentially leading to more serious security breaches. The other part of this is default user accounts or super user accounts. These were common decades ago but are now outlawed in Europe and California. This basically uses the old “Admin” account which had a default password of “Password” and went through every setup, so the setup was easy for the installer, but also almost easy for anyone to get into the system
5. Multiple connected devices
Compromised devices can serve as a means of penetrating entire networks, giving hackers unauthorized access to sensitive information or monitoring critical systems Regularly updating devices in offices and homes to prevent vulnerabilities potential edge is critical to organizations and individuals Understand and follow appropriate safety procedures.
6. Lack of encryption
Unsecured IoT devices are vulnerable to hackers who know the vulnerabilities that need to be identified to control devices and can cause serious damage or be used as entry points into large networks If IoT devices are not secured , posing risks not only to the device itself but also to the privacy and security of the data are created and accessed Encryption systems are critical to maintaining the trust of users and businesses to create an IoT ecosystem is protected against cyber attacks that could lead to unauthorized access and misuse of sensitive information.
7. Network access control (NAC)
Network Access Control (NAC) keeps track of all IoT devices connected to a network, providing organizations with a solid foundation for monitoring devices and responding to anomalies
8. Segmentation
Segmentation is an approach to IoT security that allows internet-connected IoT devices to be divided into their own separate networks, and only allowed limited access to the main network. This for enterprises can effectively monitor IoT networks and detect suspicious behavior, before that can go any further.
9. Security gateways
IoT security gateways create additional protection between devices and networks. These gateways reserve the right to install barriers (such as firewalls) to prevent cybercriminals from accessing compromised devices on other connected systems.
10. Patch management and continues software updates
Finding a way to keep devices and software up to date through network connectivity or automation is critical. Systematic disclosure of vulnerabilities is also important to allow equipment upgrades as quickly as possible. Also consider end-of-life options.
11. Training
IoT and business process security is a novelty for many existing security teams. Security professionals must remain aware of new or unfamiliar systems, learn new systems and programming languages, and prepare for new security challenges. C-level and cybersecurity teams should receive regular cybersecurity training to keep up with modern threats and security measures.
12. Team Integration
It can be beneficial to include frequent slide groups in training. For example, having developers work with security experts can help ensure that appropriate controls are integrated into devices during development.
13. Consumer education
Making consumers aware of the risks of IoT systems and providing them with steps to stay safe, such as changing default credentials, implementing software updates with consumers could play a role in compelling device manufacturers to manufacture safe devices and refuse to use devices that do not meet high safety standards.
14. Enforcement and authorization of zero trust policies
The zero-trust model means that all users -- inside or outside the organization -- must review, authorize, and continuously verify the security policies and currencies before granting access to applications and data Automate zero -trust policies, enforce them across the board Protection against IoT devices -Can help mitigate the threat.
15. Multi Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds additional security by requiring more than one identifier when requesting access to a device or network. By introducing an MFA framework, enterprises and home users can improve the security of IoT devices.
16. Machine Learning (ML)
ML technology can be used to secure IoT devices by enabling device control and scanning across the network. Because every device connected to the network is scanned, it automatically stops attacks before alerting IT teams. That’s what happened in 2018 when Microsoft’s Windows Defender software stopped a Trojan malware attack in 30 minutes.
Also read this article : What is IoT?
How to protect systems and devices
Securing systems and devices is critical in the rapidly evolving Internet of Things (IoT) environment. Break down the key elements of IoT security and how each can be addressed:
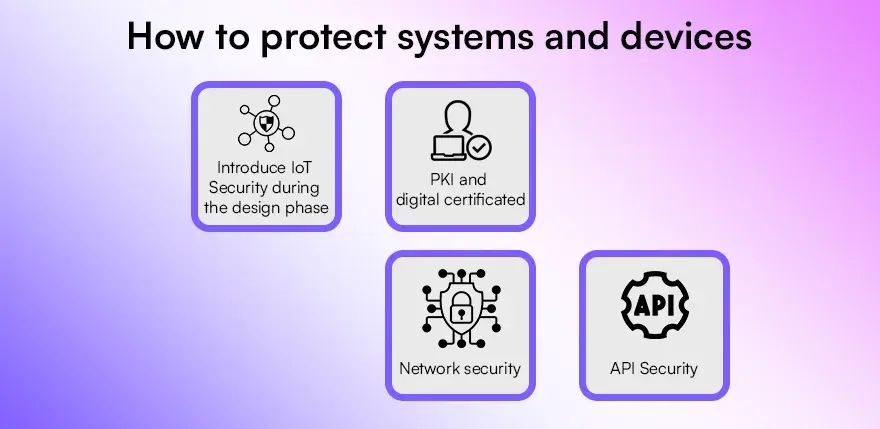
1. Introduce IoT Security during the design phase
Considered best practice for securing IoT devices and networks, this approach provides early detection and mitigation of potential security vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of intrusion unauthorized, data breaches, and other cyber threats Built-in security against known vulnerabilities to be exploited in IoT network security during the the design phase They also enable configured devices and provide the basis for security updates and patches continuous throughout the lifecycle Organizations can ensure that security measures are seamlessly integrated into device applications and operating systems, reducing the need for additional layers of security or future modifications This approach this increases the security level of IoT devices, Saves time and resources, and is more cost-effective than dealing with post-installation security issues
2. PKI and digital certificated
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a system for issuing, storing, and revoking digital certificates, which are electronic proofs of authenticity of users, devices, servers, or websites As noted above, “ culture” the PKI system essentially uses the same to generate certificates and keys on each device . The advanced model gives each property its own certificate. For example, if there are 100 people working in a building and they all have a physical key to the front door, each of them can use the key to enter. If one drops out or is expelled and doesn’t log in with his or her key, he or she can still log in. Modern buildings use unique key cards for each person, thus providing granular access. Device Authority assigns each unique key through an asset for granular, not global, authority.
3. Network security
The network provides a great opportunity for threat actors to remotely control IoT devices. Since networks incorporate both digital and physical resources, IoT security on campus must address two different modes of access. IoT network protection includes ensuring port security, enabling port forwarding and never opening ports when necessary; used in antimalware, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems; block unauthorized IP addresses; and ensuring that policies are revised and updated.
4. API Security
Application programming interfaces (APIs) are defined codes that allow applications to communicate with each other. Secure APIs can ensure that only authorized entities can access and interact with IoT devices and functionality, preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and other potential security vulnerabilities Security APIs as well as applications and IoT devices Data encryption and authentication mechanisms also play an important role in further strengthening the overall security of communications. Using secure APIs gives businesses the peace of mind knowing that their critical data is protected and their IoT ecosystem is protected from potential cyber threats.
How to address IoT security requirements?
Effectively implementing and managing IoT security requires a holistic approach. This should include a range of methods and tools and consider adjacent systems, such as networks.
There are three key components to a robust IoT security solution:
1. Learn
Use security solutions that provide network visibility to understand what risk profiles are for each class of IoT device and what the ecosystem encompasses.
2. Segment
As with network classification, use classification based on system groups and risk profiles to classify IoT systems.
3. Protect
Monitor, manage and execute an IoT security strategy that empathizes with activities at different points in the system.
Understand IoT Security Requirements
IoT security requirements support IoT security policies that are specific to business, infrastructure, and network environments. Beyond the rigor of implementing performance management, regular patches and updates, encouraging the use of strong passwords, and focusing on Wi-Fi security, there’s plenty of security there is a need to consider
Monitoring network and device behaviors to detect deviations is a best practice for identifying IoT device vulnerabilities. Another best practice is the distribution of IoT devices in networks connected to separate networks to remove vulnerabilities and threats to prevent the proliferation of vulnerable devices within the enterprise If a zero-trust network is allowed the use of which provides additional protection.
With the limited configuration capabilities of many IoT devices, instead of trying to protect IoT firmware and software, you can protect your IoT environment with security solutions that provide multiple levels of protection, including endpoint encryption
As IoT and cloud converge, consider protecting technology with new cloud-based security solutions that also add processing capabilities to the edge devices
There are many different protocols used by IoT devices, ranging from Internet protocols to network protocols to communication protocols such as Bluetooth. Understanding the protocols used by your devices can help mitigate security risks.
Companies that rely on GPS for critical operations should monitor their GPS-connected devices for security issues such as spurious GPS signals or jams.
Conduct A risk management for IoT device and systems
Attackers fall in caution. They are used by organizations that do not manage IoT devices on enterprise networks. These devices can be anything from rogue devices to neglected routers with outdated firmware. Understanding the risks of each device connected to your network and monitoring individual behavior is essential to preventing cyberattacks.
Also important for IoT security is managing all network-connected devices on the enterprise network. Finding a solution that can–within minutes–identify all IoT connections in your network should be a priority.
Implements adequate encryption and secure communications
The primary purpose of encryption is to protect the privacy of digital data stored on computer systems or transmitted over the Internet or other computer networks. IoT encryption is an important part of the security of many IoT devices. By encrypting data transactions from IoT devices, the organization stands to gain confidentiality of content, verification of results, integrity of data, and transmitter identity
Encryption is an effective way to protect data, but cryptographic keys must be maintained to keep data secure, yet accessible when needed Although IoT devices are generally not they are self-targeted and lack built-in security though, acting as interesting avenues for malware that can lead to a data breach
Data encryption is not a substitute for other information security measures, such as physical access, authentication and authorization, or network management. Data encryption is as much a risk mitigation strategy as the practice of using secure communication protocols and methods to access sensitive data.
Although IoT devices are easy to use, their communication infrastructure must have the processing power, range and reliability to accommodate the existing Internet infrastructure according to the specification of the IoT application (Wi-Fi). 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac). ) has called , etc.).
Which IoT device types are most susceptible to security risks?
Cyberattacks are used to exploit vulnerable IoT devices through techniques such as network scanning, remote code execution, and command intrusion. In the healthcare industry, medical imaging systems, patient monitoring systems, and medical device gateways account for the largest share of IoT network security issues Another area of high risk is common IoT devices such as security cameras and printers. Consumer electronics, IP phones and energy monitoring equipment are most at risk.
Which industries are most vulnerable to IoT security threats?
IoT security hacks can happen anywhere from smart homes to manufacturing plants to connected cars. The severity of an attack largely depends on the individual system, the data stored, and the context.
For example, just as an attack by deactivating the brakes on a connected car or tapping into connected healthcare devices such as insulin pumps can be deadly, so can an attack on a drug house. An IoT system monitors the cooling system monitoring can compromise drug viability if temperature changes. Similarly, attacks on critical infrastructure such as oil wells, power lines or water supplies can be devastating.
However, other attacks cannot be brought down. For example, an attack on a smart door lock could allow a burglar to enter a home. Or in other security breaches, an attacker could run malware on a companion system to delete personally identifiable information, causing havoc for those affected.
IoT attacks and security varies
IoT security strategies vary depending on the specific IoT application and its position in the IoT ecosystem. For example, IoT manufacturers from manufacturers to semiconductor companies should focus on building security into their devices from the beginning, proving hardware holes, building secure hardware , ensuring secure development, providing firmware updates and patches, and dynamic testing
Developers of IoT devices should focus on secure software development and secure integration. Hardware security and integrity are important features for users of IoT systems. Similarly, for administrators, updating systems, mitigating malware, auditing, securing infrastructure and securing credentials are key. However, for any IoT application, it’s important to weigh the security costs and risks before deploying them.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of IoT security calls for a multifaceted method that addresses numerous challenges, from far flung exposure to useful resource constraints and vulnerable passwords. By incorporating techniques along with network segmentation, encryption, and continuous monitoring, agencies can bolster their defenses against evolving cyber threats. By prioritizing IoT safety, we are able to harness the transformative capacity of related gadgets while minimizing dangers to privacy, data integrity, and overall protection.
FAQs
1. Which IoT tool kinds are maximum liable to protection dangers?
2. Which industries are most prone to IoT security threats?
3. How can people make a contribution to IoT security?
Content writer at @AssignmentGPT
Rashi Vashisth is a content writer who helps brands put their thoughts into words. She creates blogs, website content, and brand stories that are easy to understand and feel genuine. Her writing style focuses on keeping things clear and making sure the message connects with the right people.
Master AI with
AssignmentGPT!
Get exclusive access to insider AI stories, tips and tricks. Sign up to the newsletter and be in the know!

Transform Your Studies with the Power of AssignmentGPT
Empower your academic pursuits with tools to enhance your learning speed and optimize your productivity, enabling you to excel in your studies with greater ease.
Start Your Free Trial ➤Start your success story with Assignment GPT! 🌟 Let's soar! 🚀
Step into the future of writing with our AI-powered platform. Start your free trial today and revolutionize your productivity, saving over 20 hours weekly.
Try For FREE ➤